William the Conqueror’s rise from Norman Duke to English King reshaped the destiny of England through conquest, reform, and a lasting legacy.
- The Rise Of A Norman Duke In A Turbulent Europe
- Claiming The English Throne And The Battle That Changed History
- Reshaping England Through Norman Rule
- The Domesday Book And The Power Of Control
- William’s Legacy And The Dawn Of A New England
- How William’s Bloodline Changed Europe Forever
- Follow My Journey And Get Inspired To Transform Your Life For The Better
The Rise Of A Norman Duke In A Turbulent Europe
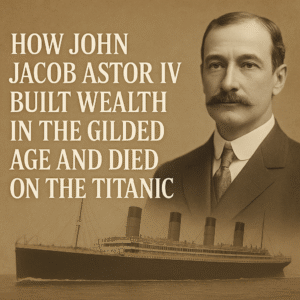
Before William became a household name in English history, he was just a boy born into the complex world of Norman politics. Born in 1028 in Falaise, Normandy, William was the illegitimate son of Robert I, Duke of Normandy, and a tanner’s daughter named Herleva. Despite his questionable lineage, William inherited the ducal title at the age of eight after his father’s untimely death during a pilgrimage to Jerusalem.
The early years of William’s rule were anything but secure. As a child duke, he was surrounded by ambitious nobles, power-hungry regents, and constant threats to his life. Yet William proved to be made of sterner stuff. He survived multiple assassination attempts and insurrections, gradually earning the respect and loyalty of his vassals through sheer resilience, tactical intelligence, and unshakable authority.
By the time he reached adulthood, William had turned Normandy into a tightly controlled duchy, enforcing law and order with an iron fist. His military successes against rebellious barons and neighboring territories earned him a reputation as a formidable warrior and a shrewd leader. But it wasn’t Normandy that would immortalize his name—it was a crown across the sea.
Claiming The English Throne And The Battle That Changed History
The death of Edward the Confessor in January 1066 without a clear heir set the stage for one of the most famous succession crises in medieval Europe. William, who claimed that Edward had promised him the throne years before, faced competition from Harold Godwinson, England’s most powerful noble and the man crowned king shortly after Edward’s death.
To William, Harold’s coronation was not only a betrayal but an act of war. Determined to enforce what he believed was his rightful claim, William sought papal approval and began amassing a formidable invasion fleet. With a blessing from the Pope and the full might of Normandy behind him, William crossed the English Channel in September 1066.
The two forces met at the Battle of Hastings on October 14, 1066. It was a brutal clash of shield walls, cavalry charges, and legendary moments. William’s strategic use of feigned retreats broke Harold’s line, and the death of King Harold—allegedly by an arrow to the eye—sealed the Norman victory. William was crowned King of England on Christmas Day in Westminster Abbey.
This single battle did more than decide a throne. It marked the end of Anglo-Saxon rule and began a new chapter in English history. William’s conquest not only changed rulers—it redefined the very fabric of the nation.
Reshaping England Through Norman Rule
Conquest was only the beginning. Once seated on the throne, William faced the daunting task of consolidating his rule over a restless and divided land. The Norman elite, foreign to the Anglo-Saxon population, quickly replaced much of the existing English nobility. Castles sprang up across the countryside as symbols of Norman dominance and control—many of which, like the Tower of London, still stand today.
William implemented a brutal policy of subjugation, especially in the north. The Harrying of the North between 1069 and 1070 was a ruthless campaign to crush northern rebellions. Villages were burned, crops destroyed, and thousands perished. While it secured William’s control, it left a legacy of resentment that would simmer for generations.
Culturally, William’s rule brought significant changes. The Norman-French language influenced English, reshaping vocabulary and law. Feudalism was reinforced, tying land ownership directly to loyalty and service. The legal and administrative systems underwent a transformation, laying groundwork that future monarchs would build upon.
Yet William was not merely a tyrant. His governance was calculated and systematic. His reforms introduced more sophisticated tax systems, tighter royal authority, and centralised control that laid the foundations for the English monarchy’s future strength.
The Domesday Book And The Power Of Control
Perhaps William’s most enduring administrative achievement was the creation of the Domesday Book in 1086. It was a nationwide survey of land, property, livestock, and people—a feat unheard of in medieval Europe.
This extraordinary document served multiple purposes. It allowed William to assess and collect taxes efficiently. It also reinforced feudal obligations by documenting who held what land and under whose authority. In effect, it was a medieval census combined with a property audit, offering a snapshot of England’s economic landscape under Norman rule.
The Domesday Book gave William unprecedented control over his realm. It showcased his administrative brilliance and his belief that knowledge equated to power. It also reinforced the new social order: land and loyalty to the king were inseparable, and every noble now owed their wealth directly to the crown.
More than a practical tool, the Domesday Book became a symbol of William’s rule—absolute, structured, and unforgivingly precise. The level of detail and control it represented would not be rivalled in England for centuries.
William’s Legacy And The Dawn Of A New England
William the Conqueror died in 1087 in Rouen after a riding accident. His body, too large for his tomb, had to be forced in—a strange and almost symbolic end for a man who had tried to squeeze an entire kingdom into his vision of order and control.
His legacy, however, was monumental. The Norman Conquest didn’t just change a king—it reshaped English identity, law, language, and culture. The aristocracy became almost entirely Norman. The English language evolved, absorbing French vocabulary that still exists today. The church, too, was overhauled, with Norman clergy replacing Anglo-Saxon bishops.
Even England’s architecture changed forever. Romanesque design, stone fortifications, and the building of cathedrals transformed the skyline of towns and cities.
Yet William’s greatest legacy may lie in how thoroughly he established the principle of centralised monarchy. His governance laid the bedrock for future kings like Henry II and Edward I, who expanded and strengthened the English crown based on the system William built.
Though feared in his lifetime, William came to be respected by many historians for his vision, discipline, and the sheer scale of his accomplishments. His rule stands as one of the most pivotal turning points in the history of England.
How William’s Bloodline Changed Europe Forever
William’s descendants would go on to rule not just England, but vast territories across France, Ireland, and parts of Italy. The Plantagenet dynasty, which emerged from William’s lineage, ruled England for over three centuries. Monarchs like Richard the Lionheart, Edward III, and even Henry VIII all carried the blood of the Norman Conqueror.
His conquest also changed how European monarchs viewed warfare, succession, and power projection. William’s ability to launch a cross-Channel invasion and hold his claim by force of arms became a model of medieval kingship.
He forged an Anglo-Norman identity that influenced both England and France for generations. This shared heritage became especially important during events like the Hundred Years’ War, where the English monarchs laid claim to French lands based on their Norman ancestry.
And while William may not have foreseen the dynastic complexities he unleashed, his marriage to Matilda of Flanders united powerful European houses that would shape the future of the continent.
Even today, his legacy is inescapable. From the genealogies of British royalty to the foundations of common law, William the Conqueror’s shadow looms large over England and beyond.
I am working on building a passive income stream using the internet. If you would like to do the same take a look at this business by clicking here.
This business can be operated using the internet and the start up cost is low. I don’t have to leave my current employment to work on building this global business.
If you like what you see, work with me to build a passive income stream using this global business.
I do not provide personal investment or financial advice and I am not a qualified licensed investment advisor. I am documenting my online investment and financial journey and what’s working for me. Click Here to read disclaimer.
If you found value in this post and want to support my work, click here to buy me a coffee.
Subscribe to my list for valuable updates, tools, videos and articles that I will share as I come across them.
Let me know your thoughts on this post via the comments section. You can also add your insights and suggestions.
If you enjoyed reading this post or it added some value, please share it with others.

Follow My Journey And Get Inspired To Transform Your Life For The Better
“I may earn commissions as an affiliate from sponsored links within this post”